LEMS Diagnostic Overview
LEMS Diagnostic Odyssey
A 4-year journey to diagnosis
According to a 2012 cross-sectional study, the mean time to a diagnosis of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) was 4.4 years.3 The infographic below details factors that may contribute to a delayed diagnosis of LEMS.
Symptom Onset
Slow progression of disease4*
Patients may not seek medical help immediately
Nonspecific and fluctuating symptoms4
make LEMS difficult to diagnose
Clinical presentations similar to other conditions1,4
often lead to misdiagnosis
LEMS Diagnosis
Mean time to diagnosis was 4.4 years3
*Symptoms that progress rapidly could be a sign of cancer-associated LEMS.1,9 Read more about cancer and LEMS >

Emily’s Diagnostic Odyssey
Her road to diagnosis was unnecessarily long
Listen as Emily, a 33-year-old with LEMS, describes the twists and turns she encountered during her 10-month journey to diagnosis.
LEMS DIAGNOSTIC CONUNDRUM
Studies reveal that more than half of patients with LEMS received a different diagnosis first1,4
58% of patients
were previously diagnosed with a different condition at least once in a cohort of 241 adult patients with LEMS.4
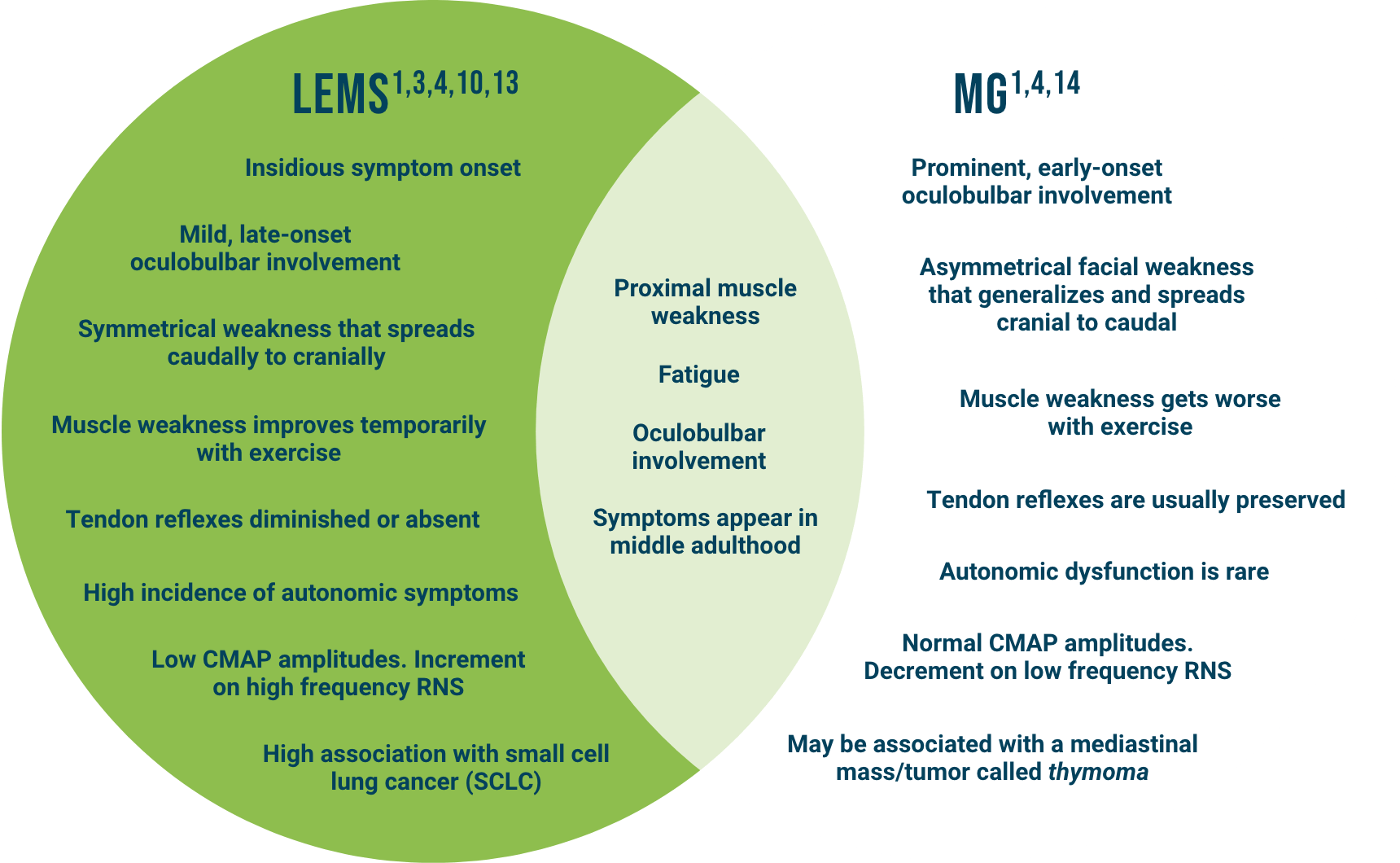
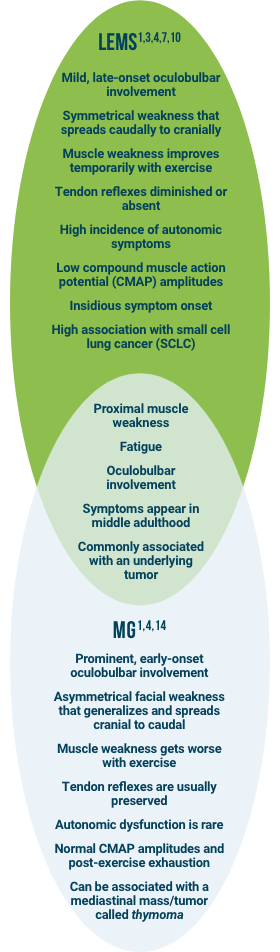
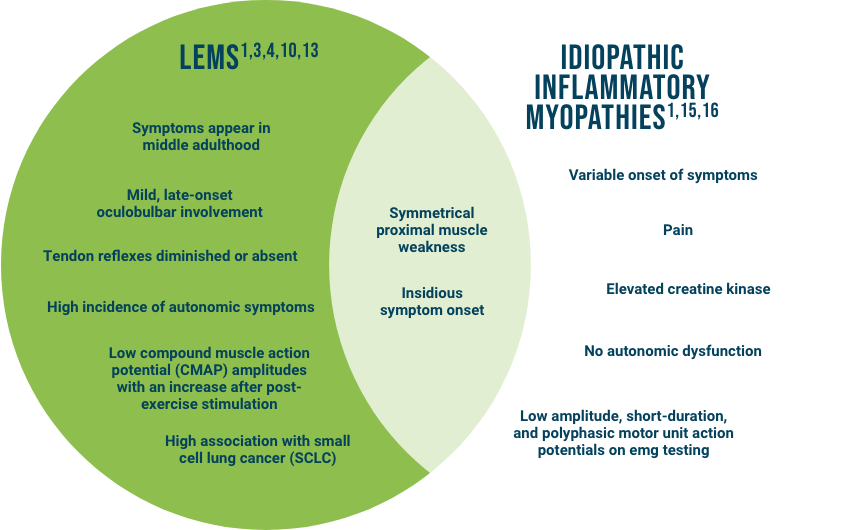
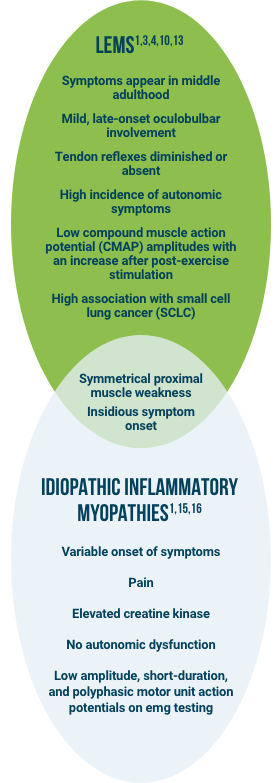
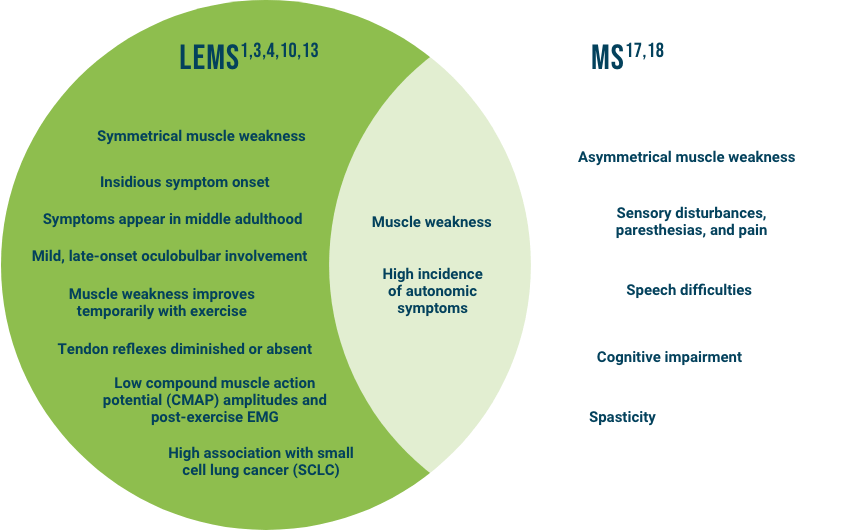
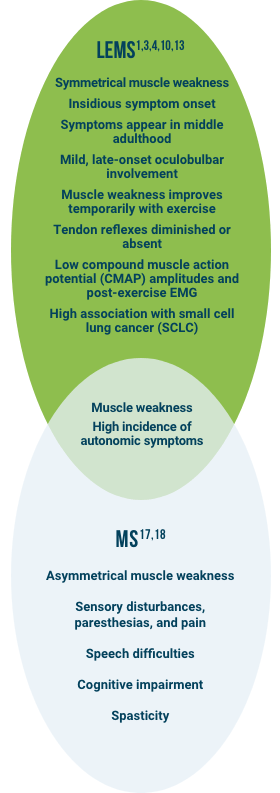
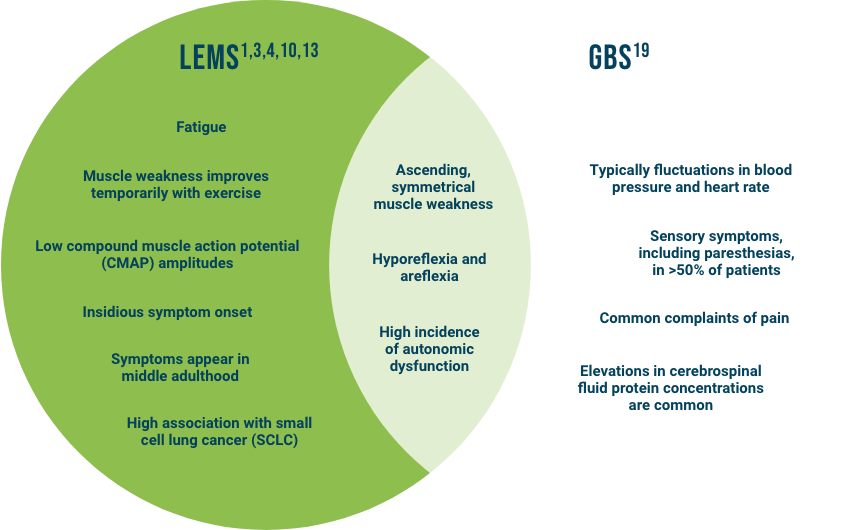
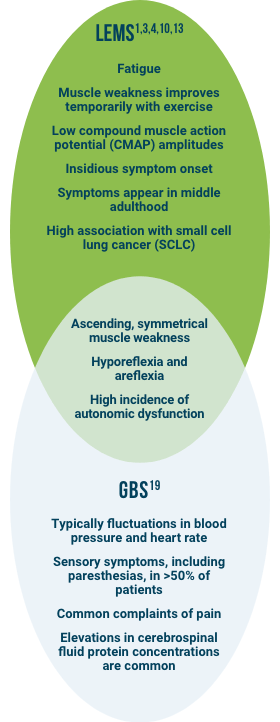
Common Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation of LEMS may resemble other common neuromuscular/neurological disorders and may be misdiagnosed as myasthenia gravis (MG), multiple sclerosis (MS), Guillain-Barré syndrome, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease.1,4